- The National Beekeeping and Honey Mission (NBHM) is a Central Sector Scheme for promoting scientific beekeeping to holistically develop the beekeeping sector. The goal is to bring about a “Sweet Revolution”.
- The mission has a total budget outlay of 500 crores and is being implemented for the period FY 2020-21 to FY 2025-26. The National Bee Board (NBB) is implementing the NBHM.
- NBHM is implemented through 3 Mini Missions that focus on productivity improvement, post-harvest management, and research & technology generation.
- In 2024, India produced approximately.4 lakh metric tonnes (MT) of natural honey.
- India exported around 07 lakh metric tonnes (MT)of natural honey worth USD 177.55 million in FY 2023-24. It is now the second-largest exporter of honey globally, up from the 9th rank in 2020.
- The Madhukranti portal has been launched for the online registration and traceability of the source of honey and other bee products.
NEW DELHI, NOVEMBER 02, 2025: The National Beekeeping and Honey Mission (NBHM) is a Central Sector Scheme launched by the Government of India for the overall promotion and development of scientific beekeeping and the production of quality honey and other beehive products. Implemented through the National Bee Board (NBB), the scheme was announced under the banner of Atmanirbhar Bharat with a total budget outlay of ₹500 crore for three years (FY 2020–21 to 2022–23). It has since been extended for another three years (FY 2023–24 to 2025–26) with a remaining budget of ₹370 crore from the original allocation.
Beekeeping, an agro-based activity undertaken by farmers and landless labourers in rural areas, forms an integral part of the Integrated Farming System. It plays a crucial role in pollination, thereby enhancing crop yields and farmers’ income while providing honey and other high-value beehive products such as beeswax, bee pollen, propolis, royal jelly, bee venom, etc., all of which serve as important sources of livelihood for rural communities.

Integrated farming (or integrated agriculture) is a commonly and broadly used word to explain a more integrated approach to farming as compared to existing monoculture approaches. It refers to agricultural systems that integrate livestock, fisheries, crop production, horticulture, etc.

India’s diverse agro-climatic conditions offer vast potential for beekeeping, honey production, and export. Recognizing its importance in rural development and agricultural sustainability, the Government of India launched the NBHM as part of the “Sweet Revolution”, an ambitious initiative aimed at promoting apiculture to accelerate the production of quality honey and boost farmers’ income through scientific and organized beekeeping.

Sub Schemes under NBHM
The NBHM is being implemented through 3 Mini Missions (MMs) – MM-I, MM-II & MM- III:
- Mini Mission-I:Under this Mission, thrust will be given on production & productivity improvement of various crops through pollination assisted by adoption of scientific beekeeping;
- Mini Mission-II:This Mission will concentrate on post-harvest management of beekeeping/beehive products including collection, processing, storage, marketing, value addition, etc. with a thrust to develop requisite infrastructural facilities for these activities; and
- Mini Mission-III:This Mission will concentrate on research & technology generation for different regions/states/agro-climatic and socio-economic conditions.
Objectives of NBHM
The main objectives of NBHM are:
- Promoting holistic growth of beekeeping industryfor income & employment generation, providing livelihood support to farm and non-farm households and to enhance agriculture/ horticulture production;
- Developing additional infrastructural facilitiesfor developing quality nucleus stock of honeybees, multiplication of stock by bee breeders and post-harvest and marketing infrastructures, including honey processing plants, storages/cold storages, collection, branding, marketing centre, etc.;
- Setting up of state-of-the-art Quality Control Labs for testing of honey & other beehive productsat regional levels and Mini/Satellite Labs at district levels in main honey producing districts/states;
- To develop blockchain/ traceability systemfor traceability of source of honey & other beehive products and using IT tools in beekeeping, including online registration, etc.;
- To develop and facilitate Honey Corridorsin potential areas;
- To promote agri-entrepreneurs & agri-startupsfor their involvement in beekeeping/honey production;
- To promote trade-agreementsbetween beekeepers & traders/honey processors/exporters, etc.;
- To promote, develop and disseminate latest technologies and skill development in beekeeping industryfor production of honey & other high value beehive products;
- Empowerment of women through beekeeping;
- To maximize, economic, ecological and social benefits by diversification through beekeepingby production of higher quantity and good quality of honey and other high value beehive products for domestic and export market; and
- To strengthen beekeepers by developing institutional frameworkthrough collective approach like formation of Self-Help Groups/Farmer Producer Organizations/Beekeepers Cooperatives/Federations, etc.
Progress and Achievements of NBHM

In Marketing Year 2024 (January to December), India produced approx. 1.4 lakh metric tonnes (MT) of natural honey. Further, the government has made several efforts to ensure the progress of NBHM:
- 6 world class Honey Testing Labs, 47 Mini Honey Testing Labs, 6 Disease Diagnostic Labs, 8 Custom Hiring centres, 26 Honey Processing Units, 12 Beekeeping Equipment’s Unit, 18 Collection-Branding& Marketing Units, 10 Packaging and Cold storage have been sanctioned under NBHM till March 2025.
- 424 hectares of land has been covered as Technology Demonstration on Beekeepingand 288 hectares as Plantations of Bee friendly Flora under the sanctioned projects of NBHM. Also, 167 activities have been sanctioned for empowerment of women by bringing SHGs under NBHM in various states.
- A National Centre of Excellencein Beekeeping has been sanctioned at IIT, Roorkee.
- As per the demand of beekeeping sector Agricultural & Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)imposed Minimum Export Price (MEP) of US $ 2,000 (Rs. 1.67 lakh) per metric ton (PMT), i.e., Rs. 167.10 per Kg for honey. The announced MEP was imposed till December 31, 2024.
- The Madhukranti portalhas been launched for online registration and traceability of source of honey and other bee products. About 14,859 Beekeepers, 269 Beekeeping and Honey Societies, 150 Firms and 206 Companies have been registered with NBB on Madhukranti portal, as of October 14, 2025.
- Under NBHM, formation of 10,000 FPOs, 100 FPOs of Beekeepers/Honey Producers are allottedto TRIFED (14), NAFED (60) and NDDB (26) for implementation of activities under NBHM. Out of total 100 FPOs allotted to NBB, 97 FPOs of Beekeepers/ Honey Producers have been registered/formed till March 2025.
- As of March 2025, a total of 298 registered producershas been benefitted by the provisions of NBHM.
Export of Natural Honey from India
India exports a variety of natural honey like Rapeseed/Mustard Honey, Eucalyptus Honey, Lychee Honey, Sunflower Honey, etc. Major Indian states producing honey are: Uttar Pradesh (17%), West Bengal (16%), Punjab (14%), Bihar (12%) and Rajasthan (9%).
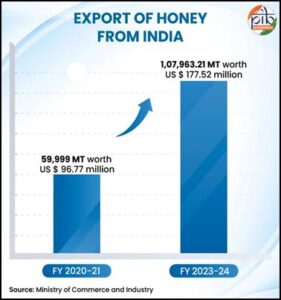
India exported around 1.07 lakh metric tonnes (MT) of natural honey worth USD 177.52 million in FY 2023-24. This is a commendable rise in exports since FY 2020-21 when India exported 59,999 MT of natural honey worth USD 96.77 million.
Major export destinations included U.S.A, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar and Libya.
As per the July 2025 Monthly Dashboard for Honey, prepared jointly by the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) and Crisil, globally, India is the second largest exporter of honey, after China, as of marketing year 2024, up from the 9th rank in 2020.
National Bee Board (NBB)
National Bee Board was registered as a society under Societies Registration Act XXI of 1860, on July 19, 2000, and was reconstituted under the Chairmanship of Secretary (A&C) in June, 2006. The main objective of NBB is overall development, promotion of scientific beekeeping in the country to increase the productivity of crops through pollination and increase the honey production for increasing the income of the beekeepers/farmers. NBB has been designated/recognized as Nodal Agency for overall development/promotion of scientific beekeeping in the country. The scheme NBHM is being implemented by NBB.
Nation-Wide Implementation Structure
| Level | Key Institutions / Committees | Main Functions |
| National Level | Mission / PMU (Project Management Unit) | Overall coordination, monitoring, and management of NBHM |
| General Council / National Level Steering Committee (GC/NLSC) | Apex body giving policy direction, review, and guidance | |
| Project Approval & Monitoring Committee (PA&MC) | Approval and monitoring of projects under NBHM | |
| Executive Committee (EC) | Examination and approval of project proposals received in NBB | |
| Project Appraisal Committee (PAC) | Appraisal and recommendation of project proposals | |
| National Level Nodal Agency | Central implementing and coordinating agency | |
| State Level | State Level Steering Committee (SLSC) | Approval, implementation, and monitoring of state-level activities |
| District Level Committee (DLC) | District-level approval, monitoring, and coordination | |
| Implementing Agencies | State Departments, NDDB, NAFED, ICAR, KVIC, TRIFED, SRLM/NRLM, MSME bodies, and NBB member institutions | Field-level implementation, training, infrastructure creation, and R&D |
Success Stories of Beekeeping from Rural India
In Nongthymmai village of Meghalaya, beekeeping has long been a traditional practice, believed to bring health and vitality to households. Once a hobby, it has now become a key source of income for many families. Shri Stevenson Shadap, who began beekeeping out of passion, transformed it into a profitable venture after receiving training through the Umsning Enterprise Facilitation Centre (EFC). By expanding his bee colonies and improving production and packaging, he now earns between ₹1 to 2 lakhs annually from honey sales in Nongpoh and Shillong markets, with demand exceeding supply. The community, inspired by his success, is forming a beekeepers’ society to enhance collective honey production, packaging, marketing, and develop value-added products. Shri Shadap remains optimistic that the Meghalaya’s Apiculture Mission will help them reach larger markets and sustain this generational livelihood.
In Kupwara district of Jammu and Kashmir, beekeeping has emerged as a major income diversification initiative through both administrative support and individual enterprise. The government has promoted the rearing of Apis mellifera bees by providing 2,000 colonies to new beekeepers at a 40% subsidy and establishing a ₹25 lakh Honey Processing and Bottling Plant at Gulgam with a daily capacity of 2 quintals, branding the produce as “Kupwara Honey” for wider markets. Local youth like Zakir Hussain Bhat, who began with five colonies, now manage over 200 colonies producing 200 quintals of honey annually and employing others. Supported by training from the government and infrastructure, over 500 farmers now produce 480 quintals of organic honey annually, generating ₹3 crore in turnover. Plans for GI tagging of “Kupwara Organic Honey” are underway to further enhance market access and prices.